A contra account is a general ledger account with a balance that is the opposite of another, related account that it is paired with.
Contra accounts are shown in the financial statements below the paired accounts, although sometimes the balances of the two accounts are merged to a net amount for presentation purposes.
Put simply, contra accounts are used to reduce the normal accounts on the balance sheet. If the related account has a debit as the natural balance, then the contra account will record a credit.
Understanding Contra Accounts
Contra accounts appear on the same financial statement as the related account. For example, an accounts receivable’s contra account is a contra asset account. This type of account can also be called the bad debt reserve or allowance for doubtful accounts.
The balance in the allowance for doubtful accounts is used to find out the dollar value of the current accounts receivable balance that is deemed uncollectible. The balance sheet shows the amount in the asset section underneath the accounts receivable. The net value of both these figures is usually reported on a third line.
The use of contra accounts ensures the accuracy of financial accounting records, as the value of the original accounts is not directly reduced. In the event that a contra account is not utilized, it can become increasingly troublesome to determine historical costs, which makes tax preparation time-consuming and difficult.
When the original dollar amount is kept in the original account and a separate account is used for recording the deduction, the resulting financial information becomes more transparent and helpful for stakeholders. For example, a building is acquired for $20,000, that $20,000 is recorded on the general ledger while the depreciation of the building is recorded separately.
Contra accounts help provide improve transparency and bring more detail in financial reporting.
Recording Contra Accounts
The first time a contra asset account is recorded in a journal entry, it is to be deducted from the expense. For example, when the credit amount in allowance for doubtful accounts increases, it is also recorded in the bad debt expense as a debit increase.
When recording assets, the difference between the asset’s account balance and the contra account balance is the book value of the asset. There are two major methods of recording a contra account.
The allowance method of accounting enables a company to determine the amount reasonable to be recorded in the contra account.
The percentage of sales method assumes that a fixed percentage of goods or services sold by a company cannot be received.
Both methods contribute to an adjustment in book value.
Types of Contra Account
There are 4 main types of contra accounts:
Contra Asset Account
The contra asset account carries a credit balance because an asset account usually has a debit balance. Such accounts are allowance for doubtful accounts and the accumulated depreciation account.
A company creates allowances for doubtful accounts to record the portion of accounts receivable which it believes it will no longer be able to collect. The amount in allowance for doubtful accounts is deducted from the accounts receivable account of a company.
The amount in the accumulated depreciation account is deducted from the assets of a company, such as buildings, vehicles and equipment. This can help anyone viewing the financial information to find the historical cost of the asset. The accumulated depreciation amount shows how much depreciation expense has been charged against an asset. Accumulated depreciation decreases the value of an asset, bringing it more in line with its market value.
Contra Liability Account
Liability accounts usually have a credit balance. Contra liability accounts such as discount on bonds payable and discount on notes payable usually carry debit balances.
The discount on bonds payable amount shows the difference between the amount of cash received when issuing a bond and the value of the bond at maturity. The discount on bonds payable decreases the value of a bond.
Bills payable or notes payable is a liability that is created when a company borrows any specific amount of money. If the company repays the loan early, the lender may provide a discount. This discount is subtracted from the total amount borrowed to better reflect the discount given by the lender.
Contra Equity Account
The amount on the equity contra account is deducted from the value of the total number of outstanding shares listed on a company’s balance sheet.
Treasury stocks is an example of a contra equity account. If a listed company purchases its own shares from the open market, it will have to debit the treasury stock account in order to record the transaction. A company might decide to purchase its stock when the board of directors feel the stock is undervalued or when it wishes to pay its shareholders dividends.
Contra Revenue Account
Sales returns, sales allowance and sale discounts are different examples of contra revenue accounts. Contra accounts such as these have a debit balance and are deducted from the total amount of a company’s revenue.
When the amount recorded in the contra revenue accounts is subtracted from the amount of gross revenue, it equals the net revenue of a company. In case a customer returns a product, the company will record the financial activity under the sales return account.
The sales allowance shows the discounts given to customers when returning the product. This is done to entice customers to keep products instead of returning them. For example, items with slight faults being sold with a discount.
When a company gives a discount to customers in an effort to convince them to buy its goods or services, it is recorded in the discount on sales account.
Contra Account Examples
Below are a couple of examples of contra accounts, and how they might be presented in the balance sheet:
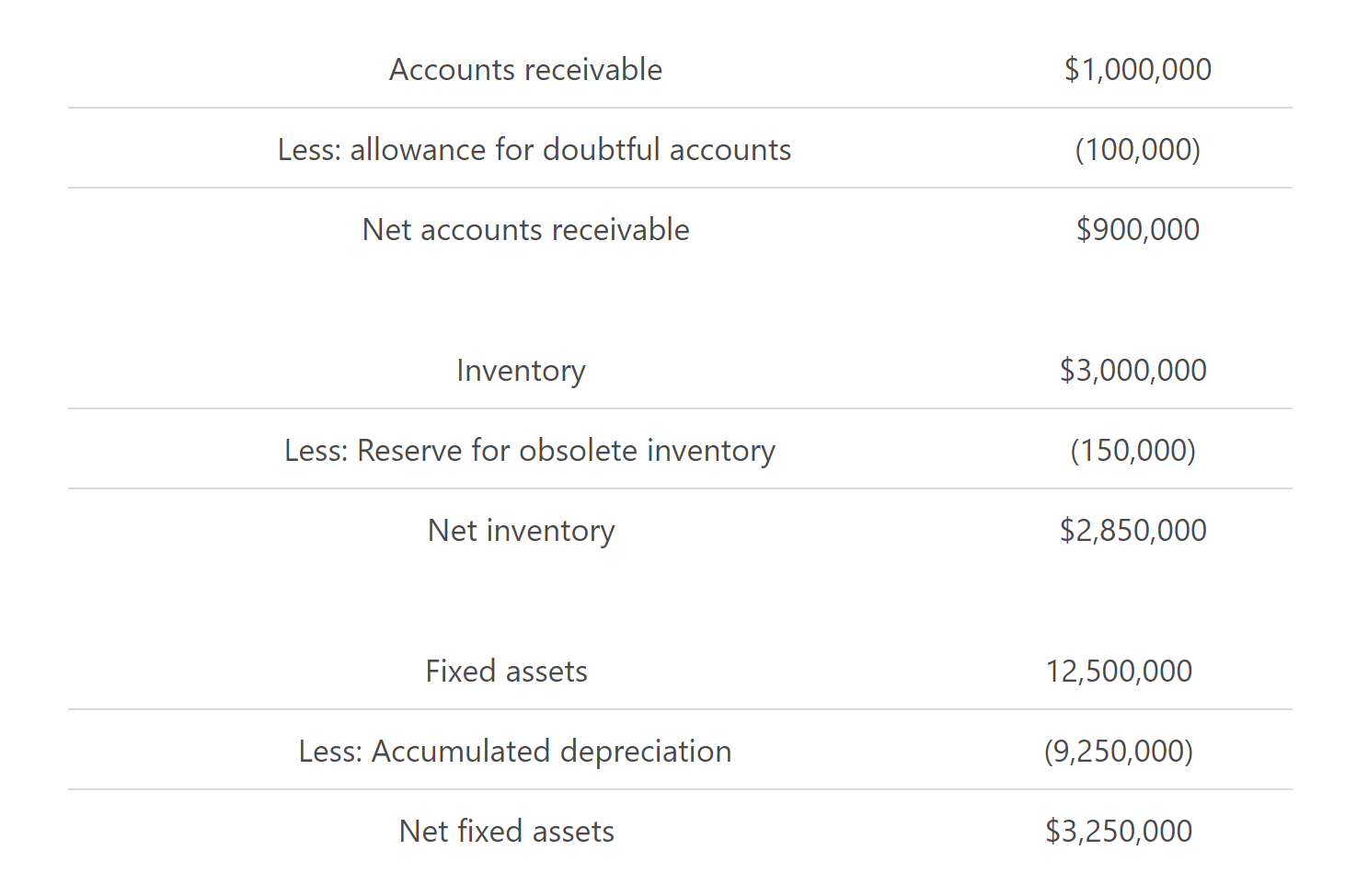
So as you can see, the contra accounts balances are reduced when the assets or liabilities they are paired with are disposed of. Put simply, when a fixed asset is sold, the accumulated depreciation that was associated with it is reversed. If this wasn’t the case, the balances of the contra accounts would just continue to increase over time.
Conclusion
Contra account is important as it not only allows a company to report the original amount of a transaction but also report any reductions that may have happened so that the net amount will also be reported. They are useful in preserving the historical value in the main account while presenting a write-down or decrease in a separate contra account that nets to the current book value. Contra accounts serve an invaluable function in financial reporting that enhances transparency in accounting books.
FAQs
1. What is a contra account?
A contra account is an account that is used to offset another account. The balance in the contra account is reduced when the corresponding asset or liability it is paired with is disposed of.
2. What are the different types of contra accounts?
There are 4 main types of contra accounts:
- Contra Asset Account
- Contra Liability Account
- Contra Equity Account
- Contra Revenue Account
3. How are contra accounts used?
Contra accounts are used to help a company report the original amount of a transaction as well as reductions that may have happened. This allows the net amount to also be reported. They serve an invaluable function in financial reporting that enhances transparency in accounting books.
4. Why should one include contra accounts on a balance sheet?
Including contra accounts on a balance sheet is important as it allows for a more transparent view of a company's financial position. This is especially true in cases where the contra account has a debit balance, as this will reduce the total amount of the corresponding account.
Another reason to include contra accounts on a balance sheet is to preserve the historical value of the main account. This is done by separating the decreases that have occurred in the contra account from the original transaction amount. This allows the reader to see both the current and historical book values for a particular asset or liability.
5. What are examples of contra accounts?
Examples of contra accounts include allowance for doubtful accounts, reserve for obsolete inventory, and accrued liabilities. Each of these accounts helps to offset another account on the balance sheet.
For instance, the allowance for doubtful accounts reduces the net amount of accounts receivable, while the reserve for obsolete inventory does the same for inventory. Similarly, accrued liabilities reduce the total amount of current liabilities.
