Accounts receivables are the amount for goods and services that are owed to a company, purchase made on credit. You can also use the term trade receivables.
You will account for the outstanding amount in the general ledger account called Account Receivables. The outstanding balance in the account is reported on the balance sheet of the company. If you are selling your goods on credit, you are likely an unsecured creditor for your customer. You should be cautious when selling your products on credit.
A company needs to estimate the amounts in the Account Receivable that will most like not be collected. This amount will be reported as a credit balance in the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, which is a contra-receivable account. This balance will reduce the amount of the account receivables on the balance sheet. If the amount is adjusted, the adjustment will be made in the allowance account and the Uncollectible Accounts Expenses, this account is reported on the income statement.
A sale on credit will create a record in the accounts receivable journal.

The accounts receivable balance is presented on the balance sheet after deducting any Allowance for doubtful accounts.

When cash is collected from the customer, the accounts receivable balance on the balance sheet is reduced through the following journal entry:

Understanding Accounts Receivable
This is the outstanding invoices that a company has or the amount of money that is owed to the company by the client. The business delivered a good or a service but has not yet been paid for that product or service. A customer is extended a short credit line that needs to be settled in a few days or a couple of months.
The amounts for accounts receivables are recorded in the balance sheets because there is a legal obligation from the client to pay the debt to the company. This is a current asset meaning the account needs to be settled in less than a year.
Accounts Receivable vs. Accounts Payable
Account receivables are when a customer owes the company money.
Accounts payable is when a company owes its suppliers’ money.
For example, Company 1 cleans windows for Company 2 and send a bill for their service rendered. Company 2 owes them money; this is recorded in the account payable column for Company 2. Company 1 is waiting for their money and thus records it in their account receivable column.
Benefits of Accounts Receivable
- It can measure the liquidity of the company, the company’s ability to cover its short-term obligations.
- The accounts receivable turnover ratio can be used to measure the number of times that a business receives accounts the balance of their accounts receivables in a financial year.
- The day’s sales outstanding analysis will measure the average time it takes a company to collect the receivable balance in a specific period.
Cash Generation from Receivables
Account receivables is a current asset for the company, a company can ask a bank to assist them with a loan and use the account receivables as security. A lot of companies follow this practice to ensure liquidity.
Credit Card Payments
A credit card payment is technically a receivable to a company because it takes a day or two to pay into the companies account. As soon as the money has been received, it will not be a receivable anymore.
Accounts Receivable Examples
Example 1
Electricity companies bill their clients after the clients have utilized the electricity. The company will make records of the account receivable, all the unpaid invoices that the client needs to pay.
The company mostly operate with a percentage of their sales on credit. Usually, a company would offer credit to frequent or exclusive customers. It makes the transaction easier for your clients, and the company could offer their clients a discount if they pay early.
Example 2
A company delivers 50 chocolates to their customer on the 1st of February and allows the customer to only pay after 30 days. On the 1st of February, the amount for the 50 chocolates will be entered into the accounts receivable journal until the account has been paid.
Example 3
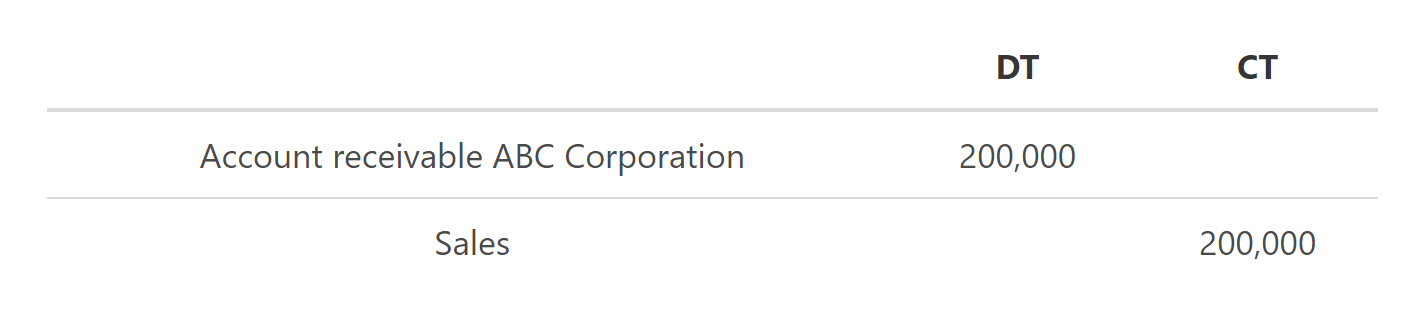
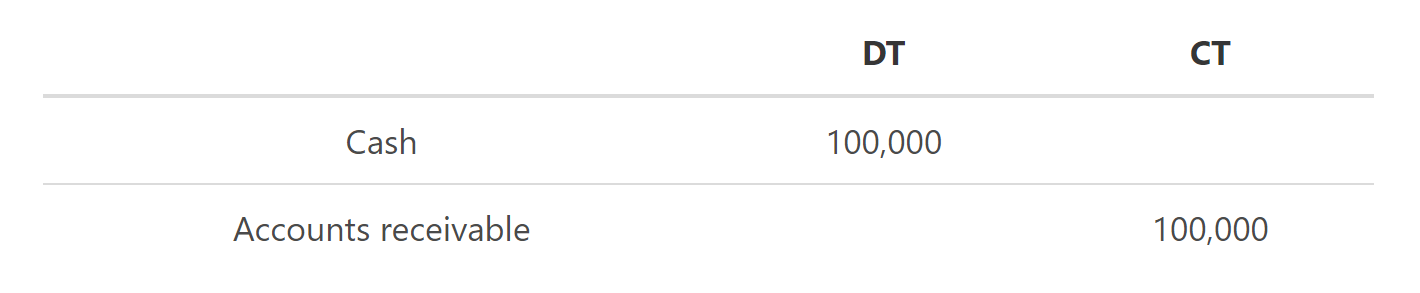
Incredible Software developed a software tool for ABC Corporation for the value of $200 000, which ABC Corporation needs to pay 30 days after the development team has successfully delivered the system. Successful testing was concluded on the 30 of April, and the software launched. ABC Corporation made a payment of $100 000 on the 16th of May.
A different liability needed to be settled by ABC Corporations in April, making it impossible for them to pay the full amount owed to Incredible Software. The outstanding amount is recorded in Incredible Software’s book as an account receivable.
The sale of software and related services is recorded through the following journal entry:
Payment by ABC Corporations on 16 May is journalized as follows:
Accounts Receivable Conclusion
- Account receivables are the amount for goods and services that are owed to a company, purchase made on credit.
- You will account for the outstanding amount in the general ledger account called Account Receivables.
- The outstanding balance in the account is reported on the balance sheet of the company.
- Accounts receivables are when a customer owes the company money.
- Accounts payable is when a company owes its suppliers’ money.
- Benefits of account receivables
- It can measure the liquidity of the company, the company’s ability to cover its short-term obligations.
- The accounts receivable turnover ratio can be used to measure the number of times that a business receives the balance of their accounts receivables in a financial year.
- The day’s sales outstanding analysis will measure the average time it takes a company to collect the receivable balance in a specific period.
- Account receivables is a current asset for the company, a company can ask a bank to assist them with a loan and use the account receivables as security.
- A credit card payment is technically a receivable to a company because it takes a day or two to pay into the companies account.
FAQs
1. What is an Accounts Receivable (AR)?
Accounts receivable is an asset account on a company's balance sheet that represents the total amount of money owed to a company for products or services that have been sold on credit. When a company extends credit to its customers, it records the sale as a receivable in its books. The account receivable will remain on the balance sheet until the customer pays the debt in full.
2. What are examples of receivables?
Some common examples of receivables include sales made on credit, unpaid invoices, and money owed to the company by its customers. Credit card payments are also considered a form of receivable, as it can take a day or two for the payment to be transferred from the customer's account to the company's account.
3. Is accounts receivable an asset or revenue?
Accounts receivable is an asset because it represents the money that a company is owed by its customers. When a customer pays off their debt, the account receivable is reduced and the cash is transferred from the asset account to the revenue account.
4. How are accounts receivables different from accounts payable?
Accounts payable is the opposite of accounts receivable. It represents the money that a company owes its suppliers for products or services that have been purchased on credit. Accounts payable is a liability account on the balance sheet, while accounts receivable is an asset.
5. Where do I find a company's accounts receivable?
The account receivable will be listed on the company's balance sheet under the assets section. It is usually listed as a current asset, meaning that it is expected to be collected within one year.
