Defining Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic Asset Allocation (DAA) is an investment strategy that automatically adjusts a portfolio's asset mix in response to changes in market conditions.
A portfolio manager utilizing the dynamic allocation technique evaluates current market circumstances as well as the performance of each asset type.
He uses the evaluation findings to lower the weights of assets that perform poorly and boost the weights of assets that perform well. Typically, adjustments entail cutting investments in the worst-performing asset classes while increasing positions in the best-performing asset classes.
The goal of DAA is to provide investors with the potential to earn higher returns than a more static asset allocation strategy without incurring additional risk.
How Dynamic Asset Allocation Works
The primary assumption of dynamic asset allocation is to adapt to current risks and downturns and capitalize on trends to obtain returns that outperform the desired benchmark.
The portfolio model is constructed from fundamental and technical factors, allowing fund managers to adjust their stock allocation. Typically, there is no target asset mix since investment managers can modify portfolio allocations as they see suitable.
The effectiveness of dynamic asset allocation is contingent on the portfolio manager making sound investment decisions at the appropriate time.
Investors can use dynamic asset allocation as one of several portfolio management strategies.
Among the metrics that may be evaluated for determining the debt-equity mix at any time are the interest rate cycle, equity values, the asset class's medium to long-term outlook, and so on.
Dynamic Asset Allocation Example
Assume global stocks undergo a six-month downturn. To mitigate risk, an investment manager utilizing dynamic asset allocation may opt to cut a portfolio's equity holdings and boost its fixed-income assets.
For example, if stocks initially dominate the portfolio, the manager may sell part of the shares and replace them with bonds. The manager may boost the portfolio's equity allocation if economic conditions improve to capitalize on a more favorable market outlook.
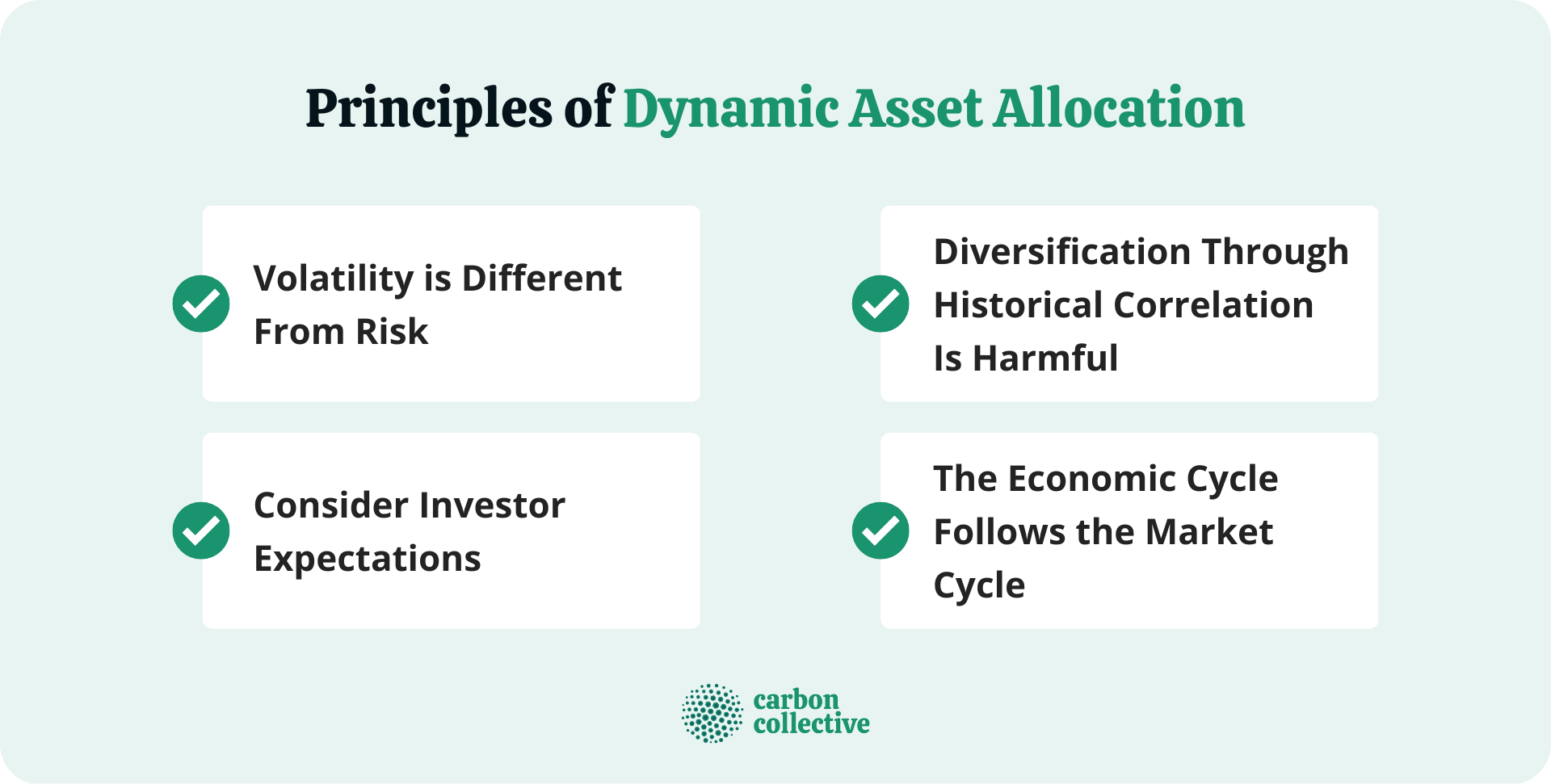
Principles of Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation is based on the following principles:
Volatility Is Different From Risk
The fundamental concept is that volatility is not synonymous with risk. Volatility is a backward-looking measurement of an asset's variability (how much its price moves around).
On the other hand, the risk is the possibility of losing money and being unable to recoup it. DAA investors should concentrate on price risk rather than backward-looking analysis such as volatility.
Consider Investor Expectations
Investors must also recognize the importance of investor expectations. High-performing firms with low volatility may face more significant adverse risks than poor-performing firms with high volatility.
High-performance firms may need help to match investors' lofty expectations. When they disappoint, their stock price drops.
However, the expectations of low-performing organizations are often smaller and more straightforward to meet. If they exceed modest expectations, their shares might be significantly re-rated.
Diversification Through Historical Correlation Is Harmful
The third point is that investors should not base their decisions on previous correlations. Correlations may shift, and they tend to rise during economic uncertainty. We frequently see popular high-priced assets become saturated.
However, when the economy turns, all investors decide to sell at that moment. Rather than considering historical correlations, investors could consider diversifying depending on asset prices and how crowded a position is.
The Economic Cycle Follows the Market Cycle
Finally, history has proven that poor economic conditions do not invariably result in poor future share market returns. If you acquire assets while the economic cycle is strong and sell them when it is terrible, you will undoubtedly lose out on opportunities and expose yourself to hazards.
Macroeconomics influences future market returns. Indeed, a sustained and long-term rise in stock prices needs robust support from profit growth and a favorable macroeconomic context.
Advantages of DAA
Several benefits can be realized by implementing a DAA strategy, which includes:
- The ability to take advantage of market cycles and trends as they occur, rather than waiting for them to end.
- A more active role in managing your portfolio can increase returns.
- Increased diversification through asset class rebalancing.
- The potential to reduce risk by selling assets when they are overvalued and repurchasing them when they are undervalued.
- The ability to take advantage of market inefficiencies.
Disadvantages of DAA
However, there are also some drawbacks associated with DAA that should be considered, which include:
- Increased complexity and costs, as DAA requires more frequent monitoring and rebalancing than traditional buy-and-hold investing.
- The need for a higher level of knowledge and expertise to make informed decisions about asset allocation.
- The possibility that incorrect market timing calls can lead to missed opportunities or losses.
Final Thoughts
DAA is a reasonably complex investment strategy that requires a higher level of knowledge and expertise than traditional buy-and-hold investing.
This works by taking advantage of market cycles and trends rather than waiting for them to end. It also involves more active management of your portfolio, which can lead to increased returns.
Dynamic asset allocation also can reduce risk by selling assets when they are overvalued and repurchasing them when they are undervalued.
While there are several advantages to implementing a DAA strategy, some drawbacks should be considered before making any decisions. These include increased complexity and costs and the need for a higher level of expertise.
Dynamic asset allocation is not suitable for everyone, and you should speak to a financial advisor to see if it is right for you.
FAQs
1. What is Dynamic Asset Allocation?
Dynamic asset allocation (DAA) is an investment strategy that determines the optimal mix of assets based on market conditions.
2. How does DAA work?
DAA takes advantage of market cycles and trends rather than waiting for them to end. It also involves more active management of your portfolio, which can lead to increased returns.
3. What are the benefits of Dynamic Asset Allocation?
Some of DAA's benefits include taking advantage of market cycles and trends, increased diversification, and the potential to reduce risk.
4. What are the disadvantages of Dynamic Asset Allocation?
DAA's drawbacks include increased complexity and costs and the need for a higher level of expertise.
5. Is Dynamic Asset Allocation suitable for everyone?
Dynamic asset allocation is not suitable for everyone, and you should speak to a financial advisor to see if it is right for you.
